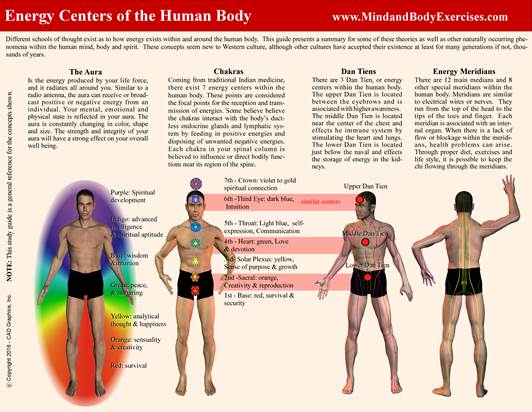
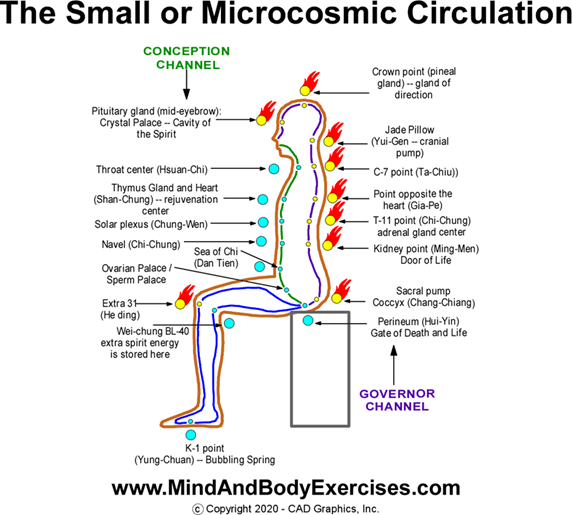
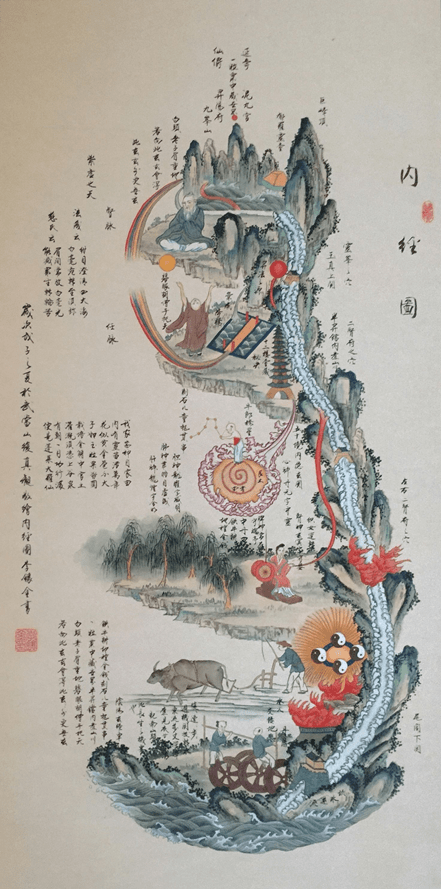
Sun-style Baguazhang founded by Sun Lutang in the early 20th century, is a unique synthesis of internal martial arts, integrating elements of:
- Xingyi Quan (Form-Intent Fist),
- Taiji Quan (Sun-style),
- and traditional Baguazhang (particularly from the Cheng style under Cheng Tinghua).
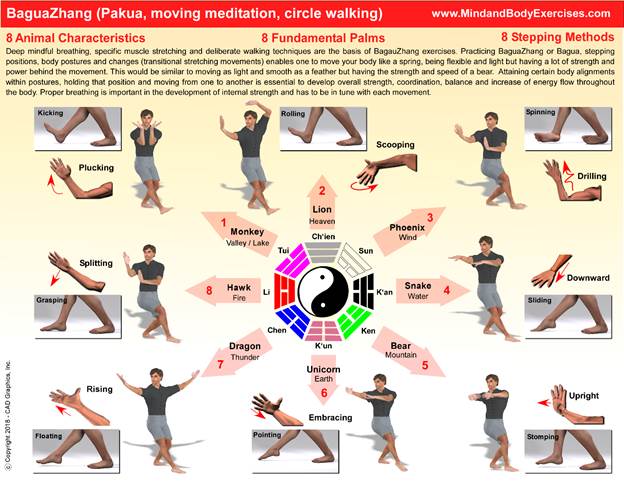
While Sun-style Baguazhang emphasizes smooth, flowing footwork, spiraling energy, and compact yet expansive movements, it also preserves the foundational concept of the “Eight Animals”, each linked to a Bagua trigram and embodying a specific energy quality, fighting method, and movement strategy.
Key Characteristics of Sun-Style Baguazhang
- Smooth, gliding footwork (“mud-wading” step is less exaggerated than in Cheng style)
- Vertical spirals rather than overt horizontal swings
- Compact circular walking and short explosive bursts
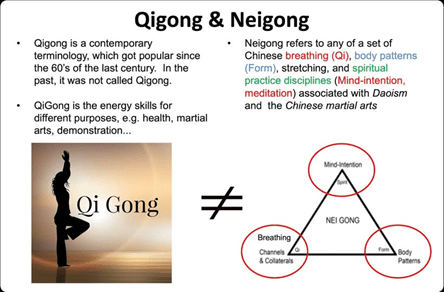
- Heavy emphasis on internal structure, breath, and intent
- More linear expressions drawn from Sun’s Xingyi Quan influence
Training Methods
- Single palm change and eight mother palms form the foundation
- Animal forms are often practiced after the basics, each representing a way to internalize energy and tactics
- Circle walking remains central, helping to refine awareness, timing, and structure
Sun Lutang’s written works, especially Baguaquan Xue (The Study of Baguazhang), emphasized the energetic and internal alchemical aspect of these animals.
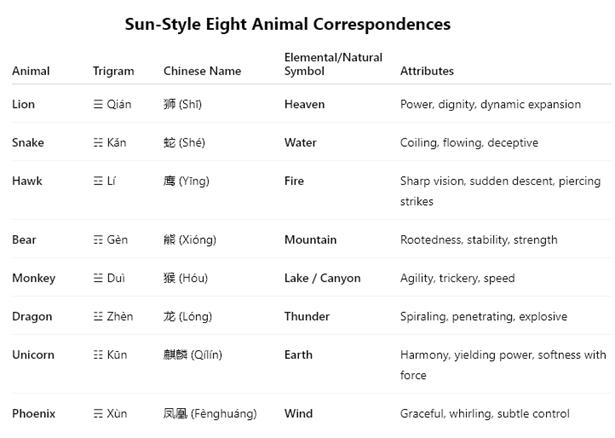
The trigrams represent both cosmological and tactical frameworks. For example:
- Dragon/Thunder (Zhèn) symbolizes suddenness, matching the explosive spirals of Dragon techniques.
- Phoenix/Wind (Xùn) represents subtle, flowing changes, aligning with evasive and redirective qualities.
- Unicorn is not just a mythical creature but symbolizes a fusion of gentleness and strength, perfect for the Earth trigram’s yielding-yet-solid essence.
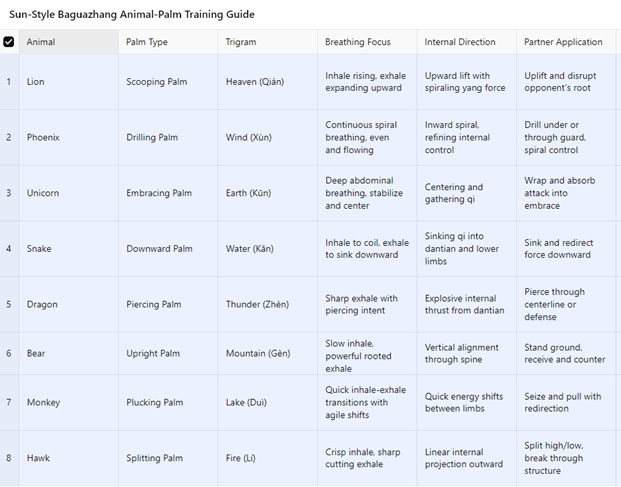
Explanation of Each Animal-Palm Correspondence
🦁 Lion – Heaven – Scooping Palm
- Heaven (Qián) is pure Yang, representing assertive, generative force from above.
- Lion’s energy is dignified and expansive. The scooping palm lifts and uproots, symbolizing Heaven reaching downward to lift Earth.
- This palm captures the rising, spiraling Yang power, useful in uprooting throws and explosive redirects.
🐦 Phoenix – Wind – Drilling Palm
- Wind (Xùn) is flexible and constant, penetrating spaces invisibly but powerfully.
- The drilling palm spirals inward and upward like a corkscrew, expressing finesse, control, and internal power.
- The phoenix as an image of transcendence and elegance matches the continuous, coiling intent of the drilling palm.
🦄 Unicorn – Earth – Embracing Palm
- Earth (Kūn) is receptive, stabilizing, nurturing, the source of all.
- The unicorn embodies gentle power, blending grace and solidity.
- The embracing palm draws in, neutralizes, and absorbs, symbolizing the earth’s ability to contain and harmonize force.
🐍 Snake – Water – Downward Palm
- Water (Kǎn) flows downward, seeks the lowest point, and adapts to all.
- The snake slithers, coils, and sinks to avoid or entrap.
- The downward palm pushes or leads energy downward, draining the opponent’s center or redirecting force into the ground, embodying water’s sinking nature.
🐉 Dragon – Thunder – Piercing Palm
- Thunder (Zhèn) is sudden, startling, and forceful.
- The dragon in Chinese cosmology often rides the thunderclouds, appearing with a burst.
- The piercing palm thrusts sharply, with intent to penetrate defenses, expressing the shock and speed of thunder, coupled with dragon’s spiral motion.
🐻 Bear – Mountain – Upright Palm
- Mountain (Gèn) is still, unmoving, and massive.
- The bear is rooted, strong, and direct.
- The upright palm rises vertically or stands firm against pressure, exemplifying the bear’s towering strength and the unwavering solidity of a mountain.
🐒 Monkey – Lake – Plucking Palm
- Lake/Canyon (Duì) is reflective, deep, and often deceptive, calm on the surface but powerful underneath.
- The monkey is clever, agile, quick to seize and let go.
- The plucking palm snatches or intercepts, sudden entry and escape, mirroring the monkey’s unpredictability and the reflective qualities of a still surface hiding motion.
🦅 Hawk – Fire – Splitting Palm
- Fire (Lí) is expansive, bright, and sharp — consuming and illuminating.
- The hawk dives with speed and precision.
- The splitting palm cleaves through space, like talons descending, fast, straight, and precise, expressing the fire-like intensity and clarity of the hawk.
Summary
Each animal-palm pairing in Sun-style Baguazhang is a holistic model:
- Trigram (Ba Gua): Provides cosmological and energetic context.
- Animal: Offers symbolic and behavioral metaphor.
- Palm: Expresses physical techniques and combat function.
This creates a threefold training method, integrating heaven (intent), earth (body), and man (expression). Practicing these palm changes while circle walking allows the practitioner to cycle through energetic qualities, mental states, and combat strategies.
References
Sun Lutang. (2013). The Study of Bagua Quan (Bagua Quan Xue) (F. Fick, Trans.). Shen Long Publishing. (Original work published 1917)
Sun Lutang. (2002). Baguaquan Xue: The Study of Eight Trigrams Boxing (J. Crandall, Trans.). Smiling Tiger Martial Arts. (Original work published 1916)
Brennan, P. (2023, January 21). THE BAGUA MANUAL OF SUN LUTANG. Brennan Translation. https://brennantranslation.wordpress.com/2015/04/30/the-bagua-manual-of-sun-lutang/