“It has always been now, it has always been you, you have always been here, the eternal consciousness momentarily residing in form.”
The Paradox of Presence
The statement above points to one of the most profound realizations of human existence, that time, identity, and consciousness are not separate phenomena but reflections of a single continuum of awareness. Philosophically, this view resonates with both Eastern metaphysics and Western phenomenology: that reality unfolds perpetually in the now, and that what we call “self” is consciousness temporarily clothed in matter. The phrase invites a dismantling of the illusion of separation between past and future, self and other, body and spirit. What remains when all temporal and spatial distinctions dissolve is pure presence where consciousness experiencing itself through form (Tolle, 1999; Advaita Vedānta, as cited in Deutsch, 1980).
The Illusion of Time and the Continuum of Now
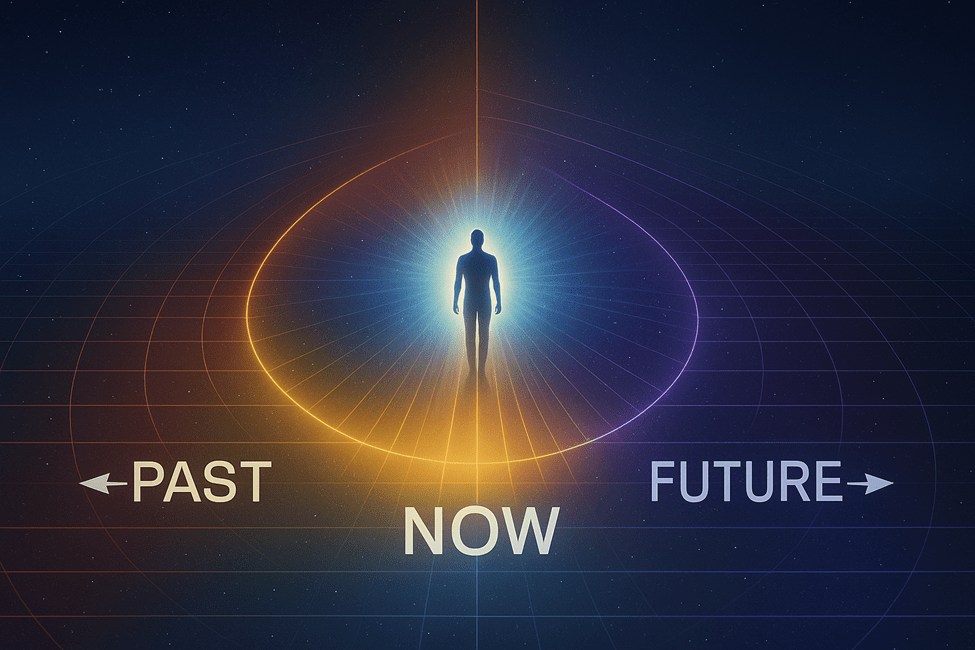
Human cognition evolved to perceive time linearly: a succession of moments divided into past, present, and future. Yet, physics and mysticism alike challenge this perception. Einstein (1955) remarked that the distinction between past, present, and future is a “stubbornly persistent illusion.” From a quantum or relativistic standpoint, all events exist simultaneously in a spacetime continuum. Similarly, Buddhist philosophy teaches that impermanence does not imply temporal fragmentation but the constant flux of a timeless now where each moment birthing the next without true separation (Nagarjuna, as translated in Garfield, 1995).
To say “it has always been now” is to step outside the psychological construct of time and into the living awareness that precedes it. In this state, “now” is not a fleeting instant but an eternal dimension as the background of all experience. Every thought, sensation, and memory arises within this unbroken field of presence. Awareness never departs; only the forms within it shift and fade like clouds across an unchanging sky.
The Self as Eternal Witness
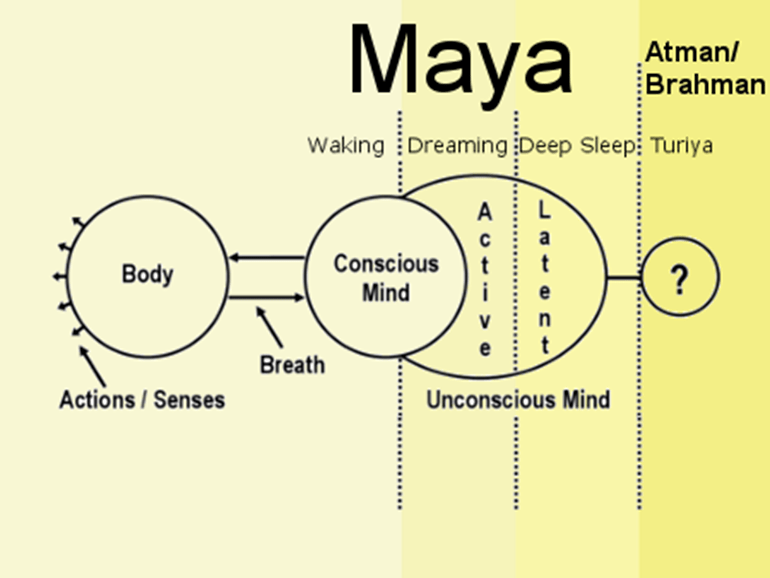
“It has always been you” is not a statement of personal identity but of essential consciousness where we are the observer behind all experiences. In Advaita and Taoist traditions, the self is not the personality but the awareness that perceives both body and mind. This is the “Atman” that is identical with “Brahman,” or the “original face before you were born,” as Zen expresses it (Suzuki, 1956). The conscious witness is silent, unbounded, and ever-present and is the same essence that animates all beings.
In Western phenomenology, Husserl and later Sartre described consciousness as “intentionality”: a self-revealing light in which objects appear (Husserl, 1931). That same light is the “you” in the aphorism and not the egoic self but the perceiving essence. When the individual realizes this, the boundary between “me” and “world” dissolves, revealing that both are movements within the same consciousness. As Alan Watts (1966) observed, “You are an aperture through which the universe is looking at and exploring itself.”
The Eternal Return of Being
“You have always been here” expresses the nonlocal and non-temporal quality of consciousness. While the body appears and vanishes in linear time, awareness, as the ground of all perception and has no beginning or end. In Taoist cosmology, the Tao is “formless yet ever-generative,” present before the birth of heaven and earth (Lao Tzu, trans. Mitchell, 1988). Similarly, Christian mysticism speaks of the “Kingdom of Heaven within,” pointing toward an eternal reality accessible through direct awareness rather than belief.
From the standpoint of experiential practices such as meditation, qigong, or contemplative stillness, one discovers that consciousness is not in the body; rather, the body is in consciousness. This reversal reveals that the witness has never left the moment or the universe it perceives. The “here” of consciousness is not a coordinate but a state of being.
Form as Temporary Expression of the Infinite
The final phrase, “the eternal consciousness momentarily residing in form,” brings the insight full circle. It affirms embodiment without attachment in that awareness chooses, or perhaps naturally manifests, as form to know itself. Matter, from this view, is crystallized consciousness; each organism is a unique configuration through which the universal intelligence experiences itself. The Tao manifests as “the ten thousand things,” yet remains unchanged in essence.
From a scientific lens, the body is a temporary aggregation of atoms forged in stars, recycled endlessly through the cosmos. The same elements that compose the body once burned in ancient suns and will again form new worlds (Greene, 2004). To realize this is to understand that life and death are merely transitions in the ongoing dance of energy where consciousness momentarily taking shape to perceive its own reflection.
The Practice of Remembering the Eternal
Philosophical insight becomes transformation only through direct realization. Meditation, breathwork, and mindful presence are methods of reuniting awareness with its source. When the mind ceases its incessant narrative of past and future, one awakens to what has never moved or the now. This awakening does not erase individuality but illuminates it with depth and humility. To live from this awareness is to act without resistance, to see oneself as both participant and witness in the cosmic unfolding.
Conclusion: The Still Point of Being
“It has always been now, it has always been you, you have always been here” points to the truth that existence is not a journey toward some future awakening but the continuous revelation of what already is. Consciousness is eternal, form is transient, and the realization of this unity is liberation. In this recognition, all striving dissolves, not into nihilism, but into reverence. The eternal consciousness does not seek permanence in form; it celebrates the impermanence through which it comes to know itself.
To awaken to this is to stand still at the center of the ever-turning wheel of time and recognize: you were never elsewhere, and you have never been anyone else.
References:
Deutsch, E. (1980). Advaita Vedānta: A Philosophical Reconstruction. University of Hawaii Press.
Einstein, A. (1955). Letter to Michele Besso. In The Born–Einstein Letters. Macmillan. https://archive.org/details/5760562-Einstein-letter-to-Besso-1951
Garfield, J. L. (1995). The Fundamental Wisdom of the Middle Way: Nāgārjuna’s Mūlamadhyamakakārikā. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780195103175.001.0001
Greene, B. (2004). The Fabric of the Cosmos: Space, Time, and the Texture of Reality. Alfred A. Knopf. https://archive.org/details/fabricofcosmossp0000gree
Husserl, E. (1931). Ideas: General Introduction to Pure Phenomenology (W. R. Boyce Gibson, Trans.). Allen & Unwin.
Lao Tzu. (1988). Tao Te Ching (S. Mitchell, Trans.). Harper & Row. https://ia600209.us.archive.org/16/items/taoteching-Stephen-Mitchell-translation-v9deoq/taoteching-Stephen-Mitchell-translation-v9deoq_text.pdf
Suzuki, D. T. (1956). Zen Buddhism: Selected Writings. Doubleday. https://archive.org/details/zenbuddhism0000dtsu
Tolle, E. (1999). The Power of Now: A Guide to Spiritual Enlightenment. New World Library.
Van Es, D. (2019, November 14). One Yoga — TripuraShakti. Tripurashakti. https://www.tripurashakti.com/one-yoga/one-yoga
Watts, A. (1966). The Book: On the Taboo Against Knowing Who You Are. Pantheon Books. https://archive.org/details/bookontabooagain00watt